The Egyptian Vulture (Neophron percnopterus), also known as the white scavenger vulture or pharaoh’s chicken, is the remaining member of the genus Neophron, It is a bird species that are found in North Africa, India, and Iberian Penisula.
In this article, I will explore with you guys everything about these birds, like where they live, what they do, what they eat, Nest, Eggs, and Young, why they need our help, and also we will explore their Taxonomy and systematics, Distribution and movements, Behaviour and ecology,
Habitat of the Egyptian Vulture:

This eagle is a versatile species that inhabits a wide range of habitats, including deserts where I live, grasslands, scrublands, semi-arid regions, and mountainous areas. he can with various ecosystems, from Plains, plateaus, mountains, etc. because he does not care about the quality of the place the important thing is that it is a desert.
even though this bird shows that he doesn’t care about the place, he prefers to live in open landscapes with a mix of vegetation types.
This eagle commonly chooses the Slopes and high places for nesting because it is safe and considered a perfect place to monitor and shoot prey, also they choose these places because usually there are a lot of corpses and carrion to provide food for their little ones.
Where do Egyptian Vulture Nest and Breed?
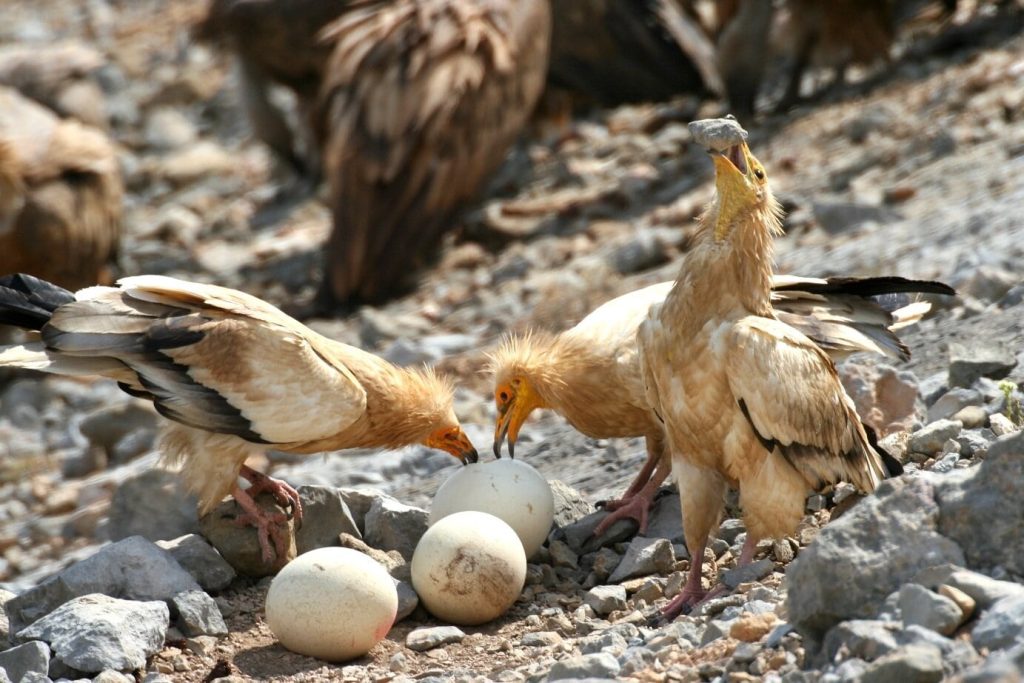

this eagle usually nests in cliff ledges, rock crevices, or sometimes in trees. they choose these places that are so hard to reach to be far away from humans, predators, and danger. they use the same nest year after year for a long time and they add some other materials each time to be more comfortable for them with their little ones.
When I was in Egypt I saw him in a rock crevice on a mountain, they were male and female with their eaglet, they were two. I really surprised by the transaction between the parents and their eaglets. they were taking care of their eaglet like human parents.
How does it construct its nest?
Based on what I saw when I was in Egypt, they construct their nests with different materials including sticks, twigs, grass, and animal bones, The nests are relatively flat and shallow with a place-like hole in the center where they put their eggs, Egyptian Vulture typically doesn’t construct nests from soft materials like feathers but he uses twigs and other things like this. he doesn’t use soft materials because of his size that big not like other small birds. so he needs something that is solid to handle his weighed.
Egg-laying and Clutch Size:
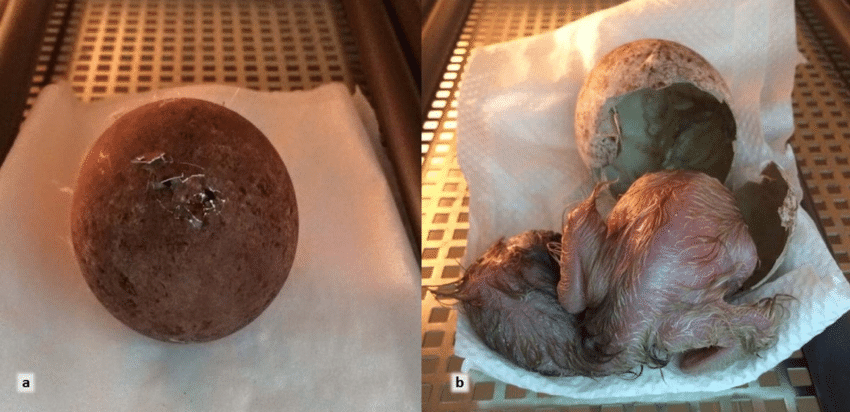

After courtship and nest building, the female Egyptian Vulture lays eggs. The clutch size can range from one to three eggs, although two eggs are the most common. The eggs are creamy-white with reddish-brown blotches, providing camouflage within the nest. The time between successive eggs being laid within a clutch is typically 2-3 days. The incubation period for Egyptian Vulture eggs lasts approximately 40 to 45 days.
How does it take care of its young?
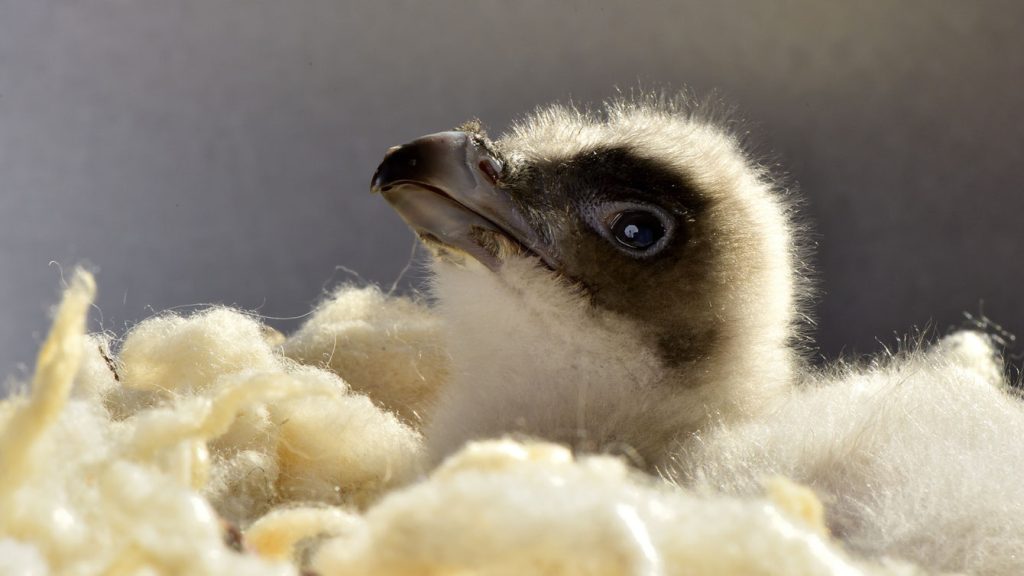

During this time the parent’s vultures take turns incubating the eggs to ensure their proper development. Both the male and female share the responsibility of incubation, with each taking shifts of several hours. while the male set on the eggs and gives them enough humidity and temperature, the female goes to look for food (carrion, and prey), and when the female goes back, the male takes turns to do the mission.
After egg hatching, they do the same process again, taking turns who will set with the little eaglet but this time not to set on the eggs, this time to give the little eaglet food, because he is so little so he can’t eat carrion, they bring the insects and worms.
Fledging and Independence:
the checks stay in the nest for a long time (70 to 90 days) in this period their feathers grow and become stronger, and trying their first attempt to fly by hopping and flapping around the nest area. Once they are able to fly the first thing that they do is explore their area in addition to training to fly well.
After this period it comes the time to go out on tours with their parents to learn how to catch mare, to be independent, and live their life without parents.
Where is the Egyptian Vulture founded?
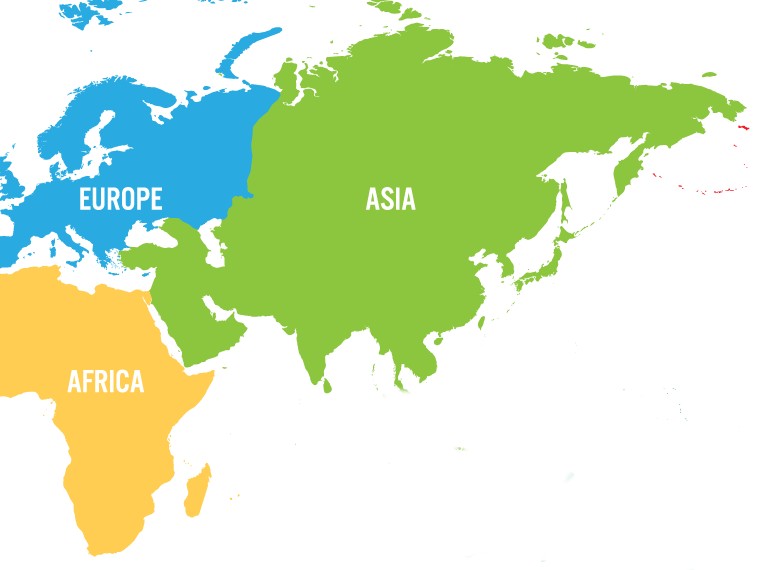
We can find Egyptian Vultures in long-range areas which are founded in (Europe, Asia, and Africa), In Africa, they occur in the northern parts of the continent, particularly in countries like Egypt, Ethiopia, Somalia, and Sudan. In Europe, it is found mainly in the southern regions, including Spain, France, Italy, Greece, and the Balkan Peninsula. In Europe, it is found mainly in the southern regions, including France, Italy, Spain, Balkan Peninsula, and Greece. In Asia, its range extends across the Middle East, from Turkey to Iran, as well as parts of the Indian subcontinent.
This bird migrates a lot between continents because of food availability and breed season, as those who are in Europe and Asia go to Africa in the winter season, but those who are in Africa do a short movement only inside the continent.
What are the threats it Faces? & How to Protect it?
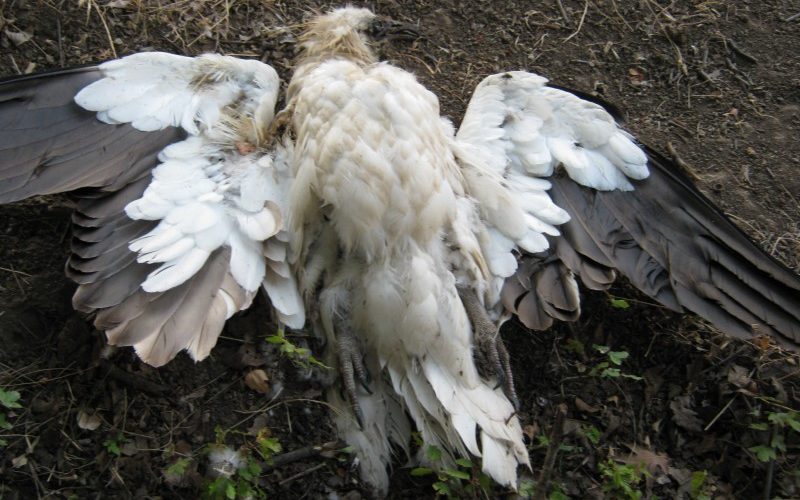

The Egyptian Vulture is listed as “Endangered” on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List. It faces numerous threats, including habitat loss, poisoning from the use of toxic pesticides, electrocution from power lines, and illegal hunting. Additionally, changes in livestock management practices and the decline in the availability of carrion, which forms a significant portion of their diet, have contributed to their population decline.
Various conservation organizations and governmental bodies are working together to protect the Egyptian Vulture and its habitat. These efforts include the establishment of protected areas, implementation of anti-poisoning campaigns, promotion of sustainable agricultural practices, and raising awareness among local communities about the importance of vulture conservation.
its formal specifications:
| Size: | 58-70 cm |
| Wingspan: | 1.5-1.7m |
| Weight: | 1.9-2.4 kg |